For generations, coffee farming was an art passed down through families, reliant on intuition and susceptible to the whims of weather. Today, a profound technological revolution is sweeping through the world's coffee lands, transforming this age-old practice. From the mountains of Yunnan to the fields of Central America, farmers are swapping guesswork for data, and tradition for innovation, to secure the future of our beloved beans in the face of climate change and market demands.
The emerging technologies in coffee farming are creating a new paradigm of precision, resilience, and traceability. They encompass advancements in plant science for climate-hardy crops, digital agriculture for hyper-efficient farm management, intelligent mechanization to overcome labor challenges, and even biotechnological breakthroughs that could redefine production itself. This isn't just about incremental improvement; it's a fundamental shift towards a smarter, more sustainable, and more profitable coffee industry.
Let's explore these groundbreaking innovations that are helping forward-thinking farms, including our own operations in Yunnan's Baoshan, produce better coffee with greater consistency and care for the environment.
How Is Plant Science Creating the Climate-Resilient Coffee of Tomorrow?
At the very root of coffee's future are scientific advancements aimed at strengthening the plant itself. With climate change threatening traditional growing regions, research is focused on developing coffee varieties that can withstand drought, heat, pests, and diseases, ensuring a stable supply for generations to come.
One frontier is the study of the coffee root system. The European Union's BOLERO research project is pioneering work to develop resilient rootstocks for coffee (and cocoa) through advanced phenotyping and microbiome analysis. By grafting high-quality coffee varieties onto these robust rootstocks, plants can gain enhanced tolerance to abiotic stresses like poor soil or drought, and biotic stresses like pests. This "open-source seeds" initiative aims to provide farmers with affordable, climate-adapted planting material, which is crucial for low-input farming systems.

Can We "Program" Coffee Plants to Withstand Stress?
Beyond traditional breeding, biotechnology is opening new doors. Researchers are exploring gene editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 to cultivate specific traits, such as heat tolerance in varieties like Caturra. The goal is to accelerate the development of plants that can thrive in shifting climatic conditions. Simultaneously, projects like BOLERO are decoding the complex relationship between coffee roots and their soil microbiome—the community of beneficial bacteria and fungi. By understanding and potentially enhancing this symbiotic relationship, scientists aim to breed plants that are naturally more efficient at nutrient uptake and more resilient to environmental stresses, reducing the need for external inputs.
What Does Cell-Cultured Coffee Mean for the Future?
Perhaps the most radical emerging technology is cell-based coffee. Companies like Israel's Pluri, through its subsidiary Coffeesai, are pioneering methods to grow coffee cells in bioreactors without the need for traditional farming. This process, which has begun pilot projects in Mexico's Chiapas region, involves establishing coffee cell lines and scaling up production in 3D bioreactors. While still in development, this technology promises a future with zero deforestation, minimal water use, and immunity to climate volatility. It represents a potential long-term solution for sustainable production, though it complements rather than replaces the art and tradition of cultivating coffee trees.
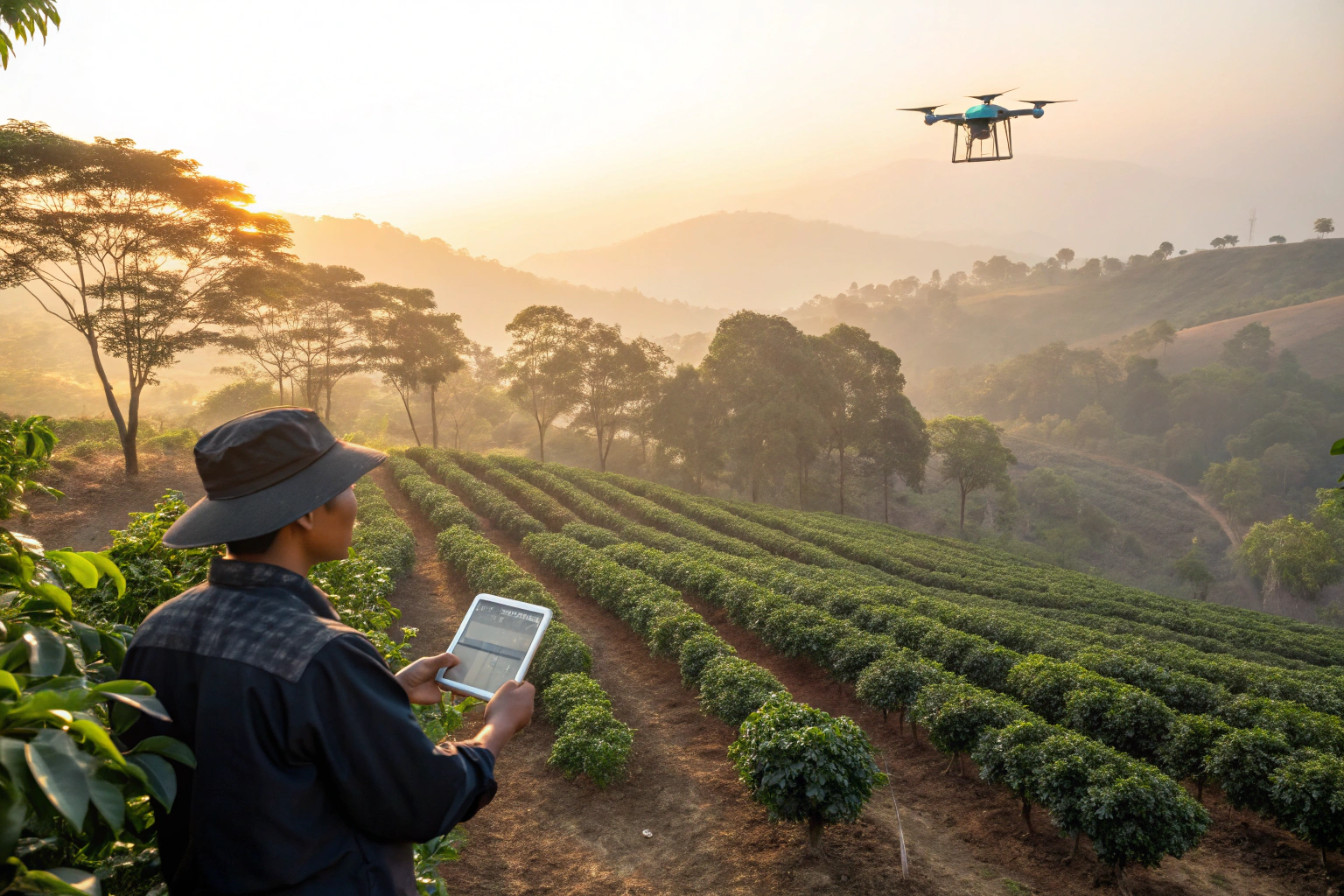
How Does Digital Agriculture Enable Precision Coffee Farming?
The concept of "precision farming" has arrived in coffee, moving from broad-stroke management to data-driven, hyper-localized care. This shift is powered by a suite of interconnected digital tools that monitor, analyze, and automatically respond to the needs of the crop.
Central to this is the deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors in the field. These devices, often solar-powered and connected via low-power networks like LoRa, continuously collect real-time data on soil moisture, nutrient levels, air temperature, humidity, and sunlight. In Yunnan, China Mobile's (Cloud Intelligent Agriculture Chain) platform exemplifies this approach, allowing farmers like Yang Jiangchun to monitor his entire farm from his smartphone and make decisions based on concrete data rather than estimation.
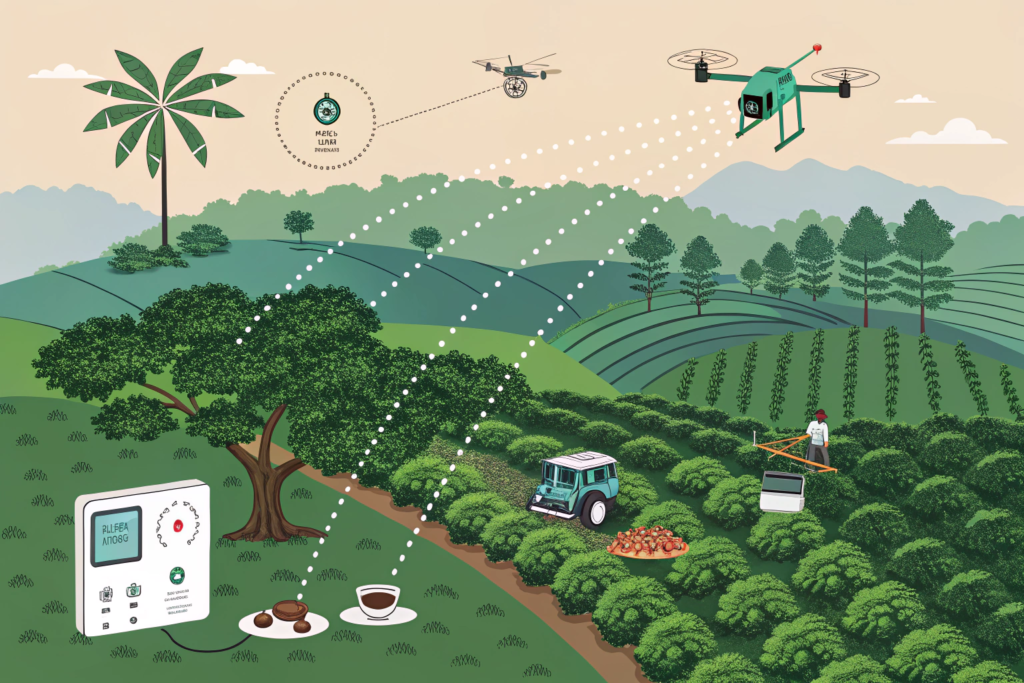
How Do AI and Big Data Optimize Every Decision?
The true power of digital agriculture lies not just in collecting data, but in interpreting it. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and big data models are now being applied to provide actionable insights. The platform, for example, uses an AI model built on agricultural expertise to analyze sensor data and offer optimized suggestions for irrigation, fertilization, and pruning schedules. This can lead to dramatic improvements: reported outcomes include a 20-21% increase in yield and a significant jump in the proportion of beans qualifying as (premium grade), from 68% to over 85%. Furthermore, drones equipped with multispectral or thermal cameras can survey vast areas, identifying pest outbreaks, nutrient deficiencies, or water stress long before they are visible to the human eye, enabling precise and timely interventions.
Can Blockchain Build Trust from Farm to Cup?
Digital innovation extends beyond the farm gate into supply chain transparency. Blockchain technology is being used to create immutable, traceable records for coffee beans. By scanning a QR code on a product, consumers can potentially see the journey of their coffee—from the specific plot where it was grown, through processing, to export. This level of transparency addresses the growing consumer demand for provenance and ethical sourcing. Studies suggest a significant portion of premium coffee consumers are willing to pay more for products with verifiable traceability, building brand trust and value.
What Role Does Intelligent Mechanization Play in Modern Coffee Farms?
Labor scarcity and high costs are critical challenges for coffee production worldwide. In response, a wave of intelligent mechanization is transforming key farming operations, from land maintenance to the delicate task of harvesting and processing.
In the field, automation is taking over arduous tasks. Autonomous weeding robots, equipped with AI for obstacle avoidance, can maintain fields around the clock, reducing manual weeding labor by at least 50%. For harvesting, which is notoriously labor-intensive, new solutions are emerging. These range from electric handheld harvesters that reduce worker fatigue to experimental laser-sorting harvesters and vibrating robotic pickers that use sensors to select only ripe cherries, vastly improving efficiency and quality.

How Is Technology Revolutionizing Post-Harvest Processing?
The period after harvest is crucial for quality but has traditionally been slow and variable. Integrated mechanization systems are changing this dramatically. A demonstration project in Taiwan showcases a full suite of machinery that automates sorting, pulping, fermentation, washing, and drying. This fully automated processing line can reduce the post-harvest timeline from the traditional two weeks down to just two days. Key machines include efficient destoners, water-saving pulpers that can process 1,000 kg of fruit per hour, and innovative mucilage removers that use 90% less water than manual washing. The result is not just speed, but unparalleled consistency and quality control in every batch.
What Are the Trade-offs Between Automation and Tradition?
The adoption of advanced technology is not without its debates. High initial investment costs for equipment like sensor networks or processing machinery can be a barrier, particularly for smallholder farmers. There are also philosophical discussions within the industry about whether technology-driven standardization might lead to a loss of the unique "terroir" and artisanal character prized in specialty coffee. The most successful applications, as seen in Yunnan's digital farms, often blend new tools with deep local agronomic knowledge, using technology to enhance rather than replace the farmer's expertise.
Conclusion
The emerging technologies in coffee farming are weaving a new future for the industry—one that is more precise, predictable, and sustainable. From the microscopic level of root microbiomes and cellular agriculture to the macroscopic view provided by drones and satellite data, innovation is empowering farmers to combat climate change, conserve resources, and produce exceptional, traceable coffee. While challenges of cost and accessibility remain, the direction is clear: the farms that embrace this smart, data-driven revolution will be the ones leading the market, offering the quality and reliability that global buyers demand.
At Shanghai Fumao, we are actively integrating these technologies on our Yunnan plantations to ensure we deliver on our promise of premium, stable, and trustworthy Arabica beans. If you are a buyer looking to partner with a forward-thinking source that invests in the future of coffee, let's connect. To explore how our tech-enhanced Catimor, Arabica, and Robusta beans can meet your needs, please contact our sales lead, Cathy Cai, at cathy@beanofcoffee.com.
